Anti forgery validation with ASP.NET MVC and Angular
February 04, 2018 by Anuraj
ASP.NET Angular CodeProject
This post is how to implement anti forgery validation with ASP.NET MVC and Angular. The anti-forgery token can be used to help protect your application against cross-site request forgery. To use this feature, call the AntiForgeryToken method from a form and add the ValidateAntiForgeryTokenAttribute attribute to the action method that you want to protect.
First you need to implement ValidateAntiForgeryTokenAttribute in Web API. Here is the implementation.
public sealed class WebApiValidateAntiForgeryTokenAttribute : ActionFilterAttribute
{
public override void OnActionExecuting(
System.Web.Http.Controllers.HttpActionContext actionContext)
{
if (actionContext == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("actionContext");
}
if (actionContext.Request.Method.Method != "GET")
{
var headers = actionContext.Request.Headers;
var tokenCookie = headers
.GetCookies()
.Select(c => c[AntiForgeryConfig.CookieName])
.FirstOrDefault();
var tokenHeader = string.Empty;
if (headers.Contains("X-XSRF-Token"))
{
tokenHeader = headers.GetValues("X-XSRF-Token").FirstOrDefault();
}
AntiForgery.Validate(
tokenCookie != null ? tokenCookie.Value : null, tokenHeader);
}
base.OnActionExecuting(actionContext);
}
}This attribute will check whether the request contains a cookie as well as a request header. If they are not the same, or either one is missing, the server knows that the post did not come from our own server and that we shouldn’t trust the input, causing an exception to be thrown. You can set this attribute in Global.asax or to specific action methods, in this blog post I am using it for POST method only.
[ResponseType(typeof(Book))]
[WebApiValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public IHttpActionResult PostBook(Book book)
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
{
return BadRequest(ModelState);
}
db.Books.Add(book);
db.SaveChanges();
return CreatedAtRoute("DefaultApi", new { id = book.Id }, book);
}To enable AntiForgeryToken in client side, I added a @Html.AntiForgeryToken() element in the Index.cshtml file. You can do it _layout.cshtml as well. This will render the token value as hidden field in the view.
<div>
<app-root></app-root>
@Html.AntiForgeryToken()
</div>Next in the Angular code, you need to read hidden field and send the value as X-XSRF-Token in the post request.
createBook() {
const httpOptions = {
headers: new HttpHeaders({
'X-XSRF-Token': $('input[name=__RequestVerificationToken]').val()
})
};
this.http.post('/api/books', this.book, httpOptions)
.subscribe(res => {
let id = res['Id'];
this.router.navigate(['/details', id]);
}, (err) => {
console.log(err);
});
}For reading the __RequestVerificationToken hidden field, I am using JQuery, since the @Html.AntiForgeryToken element is not part of Angular form, I can’t access using Angular DOM manipulation methods. To use JQuery, first you need to install JQuery (npm install jquery --save) and can be used like this.
declare var jquery: any;
declare var $: any;And here is the screenshot of client request with header and cookie value.
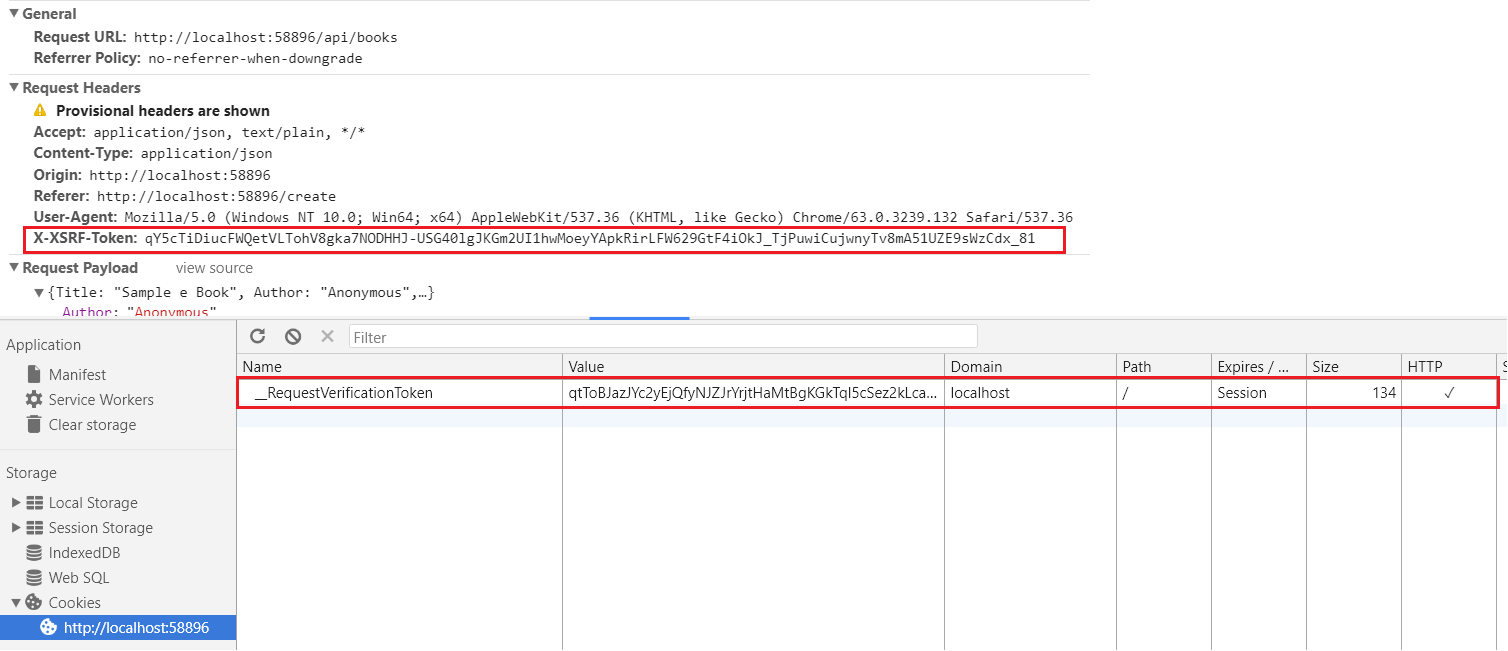
Happy Programming :)
Copyright © 2024 Anuraj. Blog content licensed under the Creative Commons CC BY 2.5 | Unless otherwise stated or granted, code samples licensed under the MIT license. This is a personal blog. The opinions expressed here represent my own and not those of my employer. Powered by Jekyll. Hosted with ❤ by GitHub