Building Sql Server Database projects with dotnet CLI
December 14, 2023 by Anuraj
DotNet SqlServer Azure
This post is about creating sql server database using dotnet CLI.
Install SqlPackage
First we need to install the dotnet tool SqlPackage. We can do it by the command - dotnet tool install -g microsoft.sqlpackage. This tool will helps to deploy the database changes to the database.
Create a SQL project
To create the Sql project, first we need to install the dotnet project templates. To install the Sql project templates we can execute the following command - dotnet new -i Microsoft.Build.Sql.Templates - this will install the Sql project templates from NuGet.org. Once we install the template, we can create the project using the following command - dotnet new sqlproj --name HelloWorld. Once the project is created, we can open the project in Visual Studio Code. Currently we can’t open the Sql Project in Visual Studio.
Next we can add table script to the file - I am using a TodoItems table script. We can add it directly to the project level. The recommended structure is like this - <Sql Object type>\<Schema>\<Name> - for this example - Tables\dbo\TodoItems.sql.
Here is the TodoItems.sql script.
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[TodoItems]
(
Id INT IDENTITY(1,1) PRIMARY KEY,
[Description] NVARCHAR(MAX),
IsCompleted BIT
)Once you add the file, we can run the dotnet build command to generate the dacpac file - which we can restore to Sql Server. Or we can use the sqlpackage tool to deploy the scripts to Sql Server.
Deploy SQL Project
To deploy the SQL project, we need to execute the following command - sqlpackage /Action:Publish /SourceFile:bin/Debug/HelloWorld.dacpac /TargetConnectionString:"Server=localhost;database=helloworlddb;User Id=sa;Pwd=SuperSecret;TrustServerCertificate=true;Connection Timeout=60;" - this command will deploy the changes to the local Sql Server. The SourceFile parameter specifies the dacpac file and the TargetConnectionString parameter specifies the Sql server connection string to deploy.
For Azure Sql Server, this command may not work because of Sql Server version issues. To fix this, open the project file and change the existing <DSP> value to this one - <DSP>Microsoft.Data.Tools.Schema.Sql.SqlAzureV12DatabaseSchemaProvider</DSP>
We can find for more details about sqlpackage command using the sqlpackage /? command.
Configuring Deployment to Azure using GitHub actions.
In GitHub actions, we can directly use SqlProj without running the dotnet build command. To do this, we can use azure/sql-action action. Here is the GitHub action.
name: Azure Database Deployment
on:
push:
branches: [ "main" ]
pull_request:
branches: [ "main" ]
workflow_dispatch:
jobs:
build-and-deploy:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Azure SQL Deploy
uses: Azure/sql-action@v2.2.1
with:
connection-string: ${{ secrets.AZURE_SQL_CONNECTION_STRING }}
path: './HelloSqlProject.sqlproj'
action: 'publish'
build-arguments: '/p:DropObjectsNotInSource=true'
Here is the screenshot of the database deployment GitHub action.
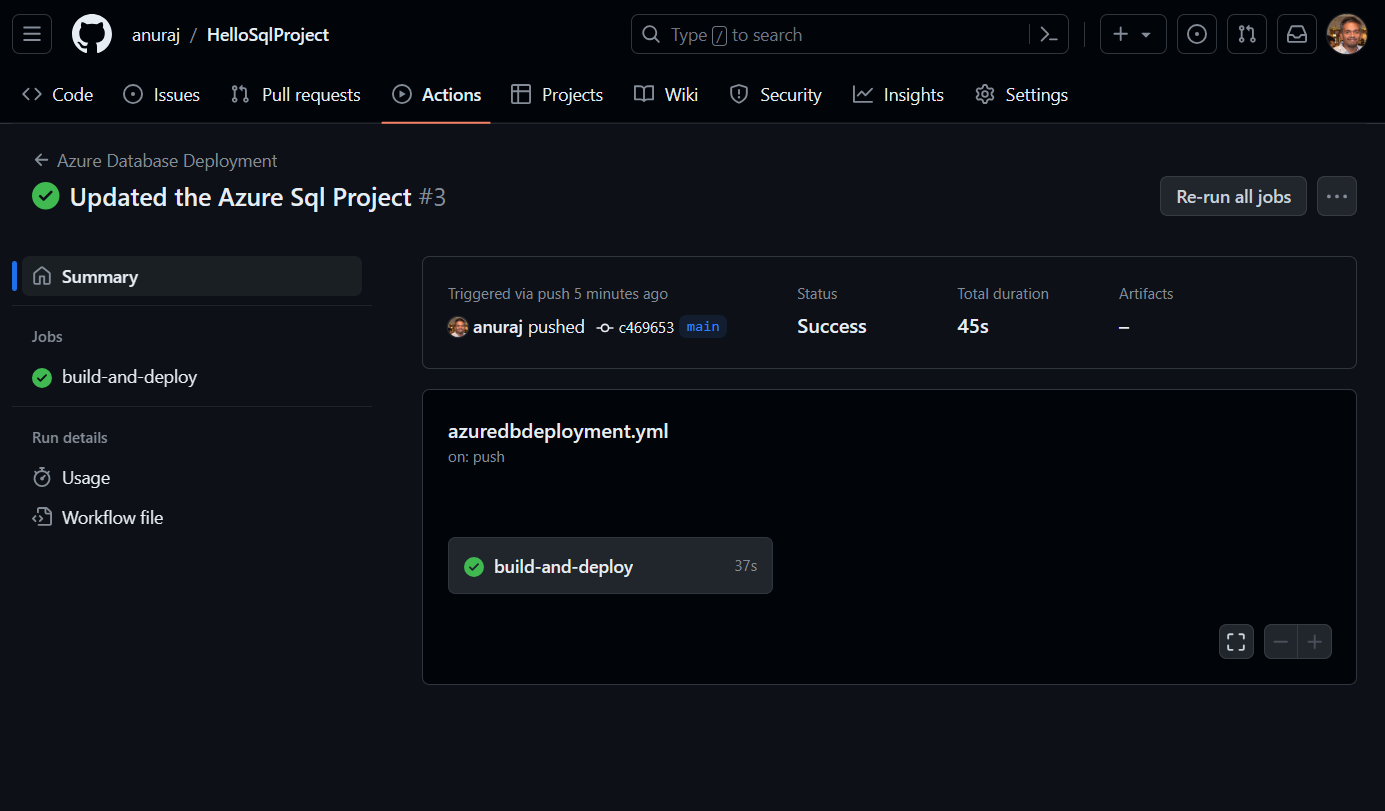
This way we can create Sql Project in SDK style - which is helpful in scenarios where we have the dedicated database development team. This way we can configure continuous deployment to Azure Sql Server using GitHub actions.
The project source and github action available here - https://github.com/anuraj/HelloSqlProject
Happy Programming.
Copyright © 2024 Anuraj. Blog content licensed under the Creative Commons CC BY 2.5 | Unless otherwise stated or granted, code samples licensed under the MIT license. This is a personal blog. The opinions expressed here represent my own and not those of my employer. Powered by Jekyll. Hosted with ❤ by GitHub