Using Azure Document DB in ASP.NET Core
April 22, 2016 by Anuraj
C# ASPNET5 ASPNET Core Azure Document DB
Azure DocumentDB is Microsoft’s multi-tenant distributed database service for managing JSON documents at Internet scale. DocumentDB indexing enables automatic indexing of documents without requiring a schema or secondary indices. DocumentDB is designed to provide real-time consistent queries in the face of very high rates of document updates. This post is about using Azure Document db from ASP.NET Core application.
To use Document DB, first you need to create Document DB from Azure portal. You can get Azure Document DB under Data + Storage.
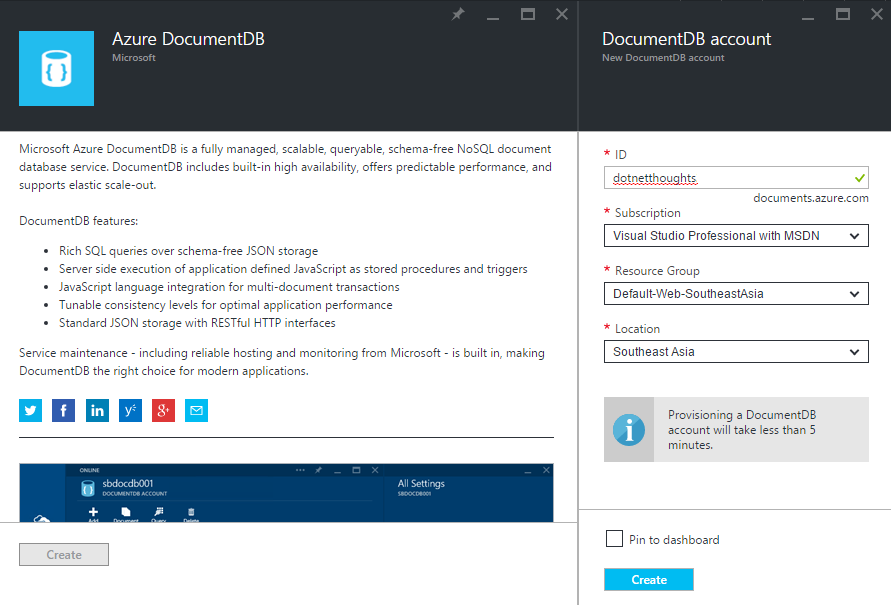
Once you create the Document DB Account, you can navigate to the Keys section and get the required keys, which is required in the application.
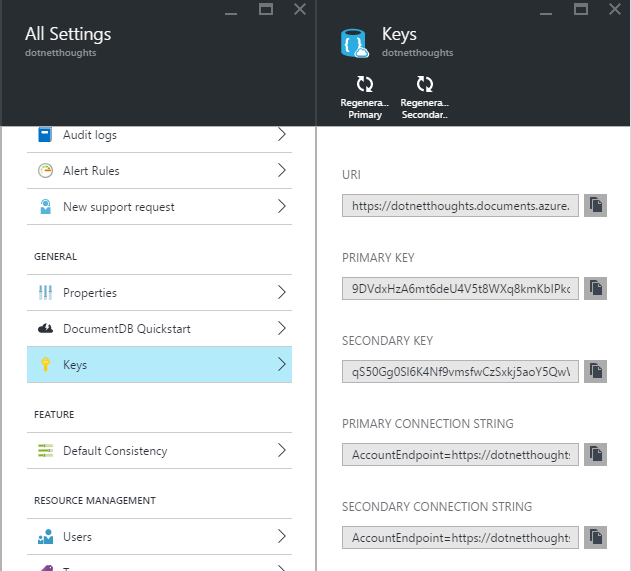
Now you completed the infrastructure configuration to use Document DB. Next you need to add the “Microsoft.Azure.DocumentDB” package in your project.json file. Here is my project.json file.
"webroot": "wwwroot",
"dependencies": {
"Microsoft.AspNet.Diagnostics": "1.0.0-rc1-final",
"Microsoft.AspNet.Hosting": "1.0.0-rc1-final",
"Microsoft.AspNet.Mvc": "6.0.0-rc1-final",
"Microsoft.AspNet.Server.WebListener": "1.0.0-rc1-final",
"Microsoft.AspNet.StaticFiles": "1.0.0-rc1-final",
"Microsoft.AspNet.IISPlatformHandler": "1.0.0-rc1-final",
"Microsoft.Azure.DocumentDB": "1.6.3"
},
"commands": {
"web": "Microsoft.AspNet.Server.WebListener"
}You can use DocumentClient class to execute query against your Document DB account. Here is the initialization code, which creates database and collection if not exists. I am using this code in controller constructor. And here is my controller code.
private const string EndpointUri = "<END POINT URL>";
private const string PrimaryKey = "<PRIMARY KEY>";
private DocumentClient _client;
private static readonly string DatabaseId = "EmployeeDb";
private static readonly string CollectionId = "Employees";
public EmployeeController()
{
_client = new DocumentClient(new Uri(EndpointUri), PrimaryKey);
CreateDatabaseIfNotExistsAsync().Wait();
CreateCollectionIfNotExistsAsync().Wait();
}
private async Task CreateDatabaseIfNotExistsAsync()
{
try
{
await _client.ReadDatabaseAsync(UriFactory.CreateDatabaseUri(DatabaseId));
}
catch (DocumentClientException e)
{
if (e.StatusCode == System.Net.HttpStatusCode.NotFound)
{
await _client.CreateDatabaseAsync(new Database { Id = DatabaseId });
}
else
{
throw;
}
}
}
private async Task CreateCollectionIfNotExistsAsync()
{
try
{
await _client.ReadDocumentCollectionAsync(
UriFactory.CreateDocumentCollectionUri(DatabaseId, CollectionId));
}
catch (DocumentClientException e)
{
if (e.StatusCode == System.Net.HttpStatusCode.NotFound)
{
await _client.CreateDocumentCollectionAsync(
UriFactory.CreateDatabaseUri(DatabaseId),
new DocumentCollection { Id = CollectionId },
new RequestOptions { OfferThroughput = 1000 });
}
else
{
throw;
}
}
}And here is CRUD application code, by default all the methods are async, so I am using async controller actions. Here is the Index action method, where I am returning all the employees in the Document DB collection.
public async Task<IActionResult> Index()
{
var query = _client.CreateDocumentQuery<Employee>
(UriFactory.CreateDocumentCollectionUri(DatabaseId, CollectionId)).AsDocumentQuery();
var results = new List<Employee>();
while (query.HasMoreResults)
{
results.AddRange(await query.ExecuteNextAsync<Employee>());
}
return View("Index", results.ToList());
}Here is the details code, where I am getting details of an employee by Id.
public async Task<IActionResult> Details(string id)
{
if (id == null)
{
return new HttpStatusCodeResult(400);
}
var employeeResponse = await _client.ReadDocumentAsync
(UriFactory.CreateDocumentUri(DatabaseId, CollectionId, id));
var employee = (Employee)(dynamic)employeeResponse.Resource;
if (employee == null)
{
return new HttpStatusCodeResult(404);
}
return View("Details", employee);
}And here is the code for Create, Update and Delete. Unlike SQL databases, there is no Id generated automatically, so it is better to create an Id field and assign guid values.
await _client.CreateDocumentAsync
(UriFactory.CreateDocumentCollectionUri(DatabaseId, CollectionId), employee);
await _client.ReplaceDocumentAsync
(UriFactory.CreateDocumentUri(DatabaseId, CollectionId, employee.Id), employee);
await _client.DeleteDocumentAsync
(UriFactory.CreateDocumentUri(DatabaseId, CollectionId, id));And here is the namespace references required.
using Microsoft.Azure.Documents;
using Microsoft.Azure.Documents.Client;
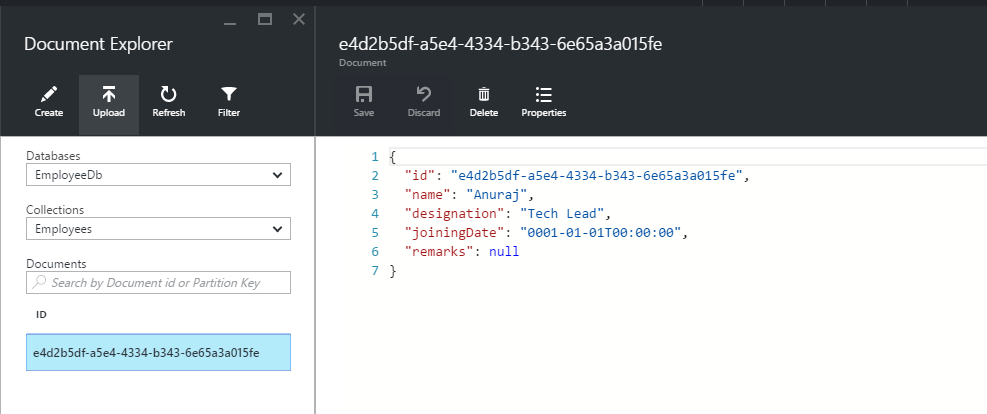
using Microsoft.Azure.Documents.Linq;Once you created any document in Document DB, you can view it in Azure portal, Document DB explorer feature.
Happy Programming :)
Copyright © 2024 Anuraj. Blog content licensed under the Creative Commons CC BY 2.5 | Unless otherwise stated or granted, code samples licensed under the MIT license. This is a personal blog. The opinions expressed here represent my own and not those of my employer. Powered by Jekyll. Hosted with ❤ by GitHub